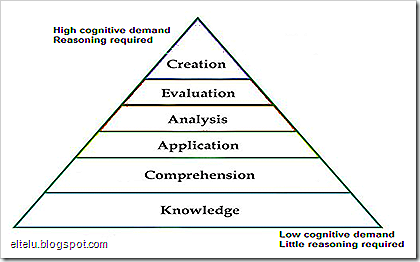
Remembering
Questions of this level are the most frequently used in the first stages of English learning, because students are at the first level of English language acquisition. Answers to the questions can be made using yes/no or embedded answers. Flashcards and drawings will help students give the correct answer. Remember (recognition), match, list, sing, color, chant etc. are typical activities at this level.
Comprehending
At this level students can understand the facts. In primary we use this level of questioning a lot. We ask students to describe, complete, illustrate or draw.
Applying
At this level students might need scaffolding and word banks to solve several problems by using previously learned facts in a different way. We ask students to choose, construct, explain, organize, plan, select, solve, and identify.
Analysing
At this level students have not got enough vocabulary and language to express responses in English. So they will need teacher scaffolding to classify, contrast, categorize, sequence and interpret facts.
Evaluating
At this level teachers have to modify the language of the questions to be simplified, but the task should remain the same. Some tasks at this level are giving opinions, making judgments about stories, comparing and evaluating the work of classmates in English.
Creating
Students will need lots of support and scaffolding to answer questions at this level, because they are asked to compile information in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern. Synthesis is particularly difficult. Some tasks at this level are to combine, create, design, develop, imagine, make up, predict and solve.
Five steps of the problem-posing methodology
1. Describe the content of discussion.
2. Define the problem.
3. Personalize the problem.
4. Discuss the problem.
5. Discuss the alternatives of the problem.
Sample activity 1: problem posing
- Topic
Cleanliness - Objectives
Think creatively and critically to find solutions to problems based on logical reasons - Task
Based on the picture (a picture of unattended waste bin) given:
Why are there so many 'things' flying over the bin?
Where have you seen this scenery?
Do you feel that this picture reflects cleanliness? Why?
What is the one thing that is needed to ensure cleanliness in the places that you have mentioned?
Sample activity 1: decision-making
- Topic
Anwar Ibrahim's Corruption Trial - Objectives
Think creatively and critically
Decision making based on logical reasons - Task
You are the judge for Anwar Ibrahim's corruption trial. You have heard the evidences and closing submissions by the prosecutors and the defense counselors. You have to give your verdict for this trial based on the evidences and submissions provided by both parties. (Note: Teachers need to provide the evidences. They also need to display impartiality on this issue).
But before you give your verdict, consider these procedures:
Can this trial be thrown out? Why?
Does this trial have to go on? Why?
Is he guilty? Why?
Is he innocent? Why?
What is your verdict? Why?
If found guilty, what is the sentence that you want to pass?
Encouraging learners to think about thinking
When Learners Say: 'The verdict is, guilty as charged.' Teachers Say: 'Describe the steps you took to arrive at that answer.'
When Learners Say: 'I don't know how to solve this question.' Teachers Say: 'What can you do to get started?'
When Learners Say: 'I am ready to begin.' Teachers Say: 'Describe your plan of action.'
When Learners Say: 'I like the large one the best.' Teachers Say: 'What criteria are you using to make your choice?'
When Learners Say: 'I am finished.' Teachers Say: 'How do you know you're correct?'
 10 Juli 2013
10 Juli 2013